Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates are considered as the most efficient solution for high power and high heat loads.
Atherm is able to design and supply many types of cooling plate technologies with liquid circulation from prototypes to mass production.
Liquid cold plates : how it works
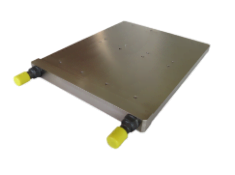
Liquid cold plates allow the cooling of any type of electronic component thanks to the circulation of a liquid inside a metal plate. The working fluid is usually a mix of water and glycol but several fluids can be used (oil, dielectric oil, naval application fluids).
The optimized and direct contact with the metal cold plate helps to dissipate the power from the component to the fluid circulating into the cold plate chanels.
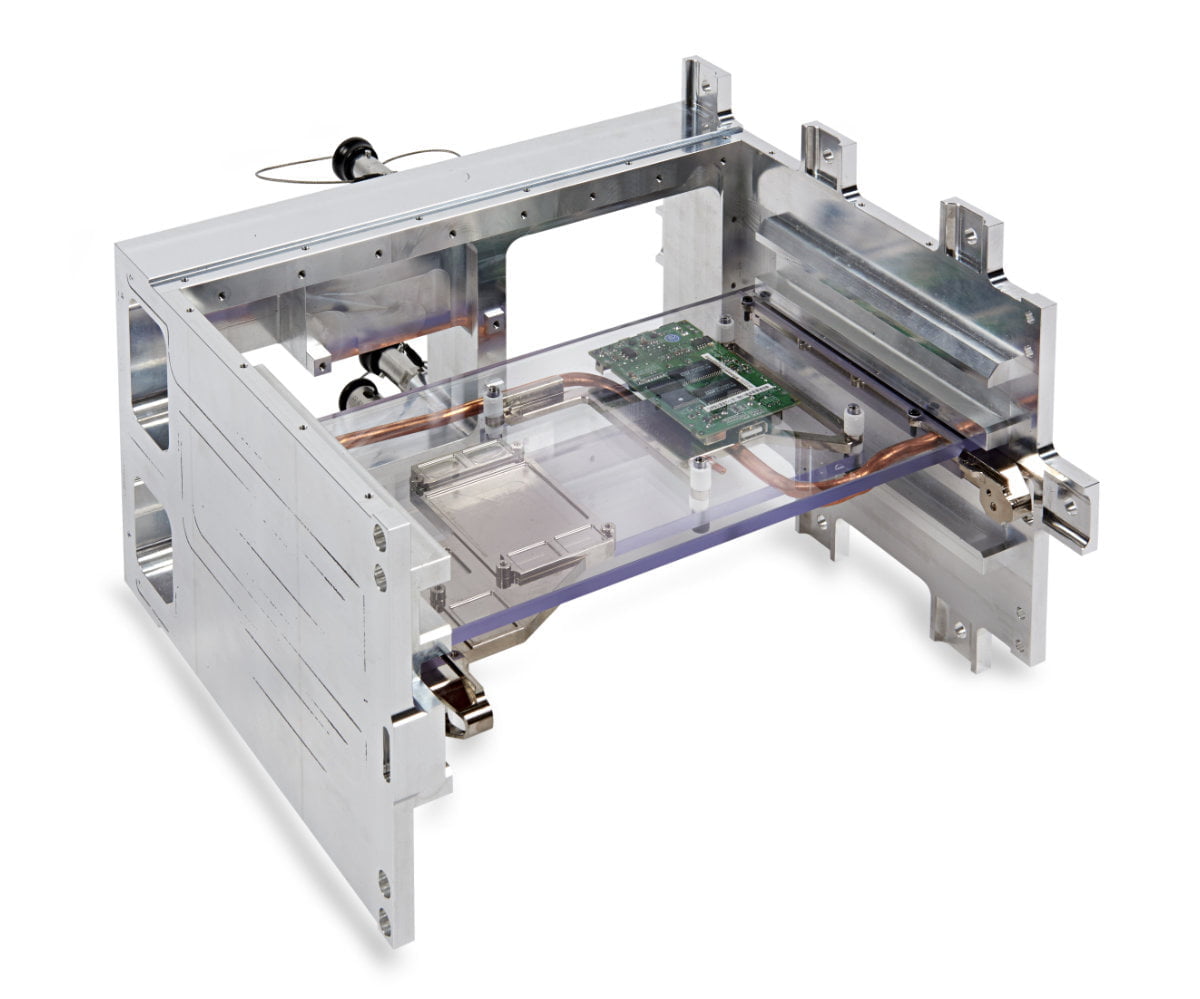
These cooling devices often integrate an optimized thermal functions’ system in order to improve the thermal exchange and the homogeneity of the temperature under the component.
The liquid cold plates are connected to a cooling loop (made up with a pump, an expansion tank and a dissipator) to allow power dissipation outside the components room or cabinet.
Designed upon your specification, the liquid cold plate characteristics are the result of our thermal calculation and experience.
Liquid cold plates : many advantages
- Up to several kW dissipated power
- Large range of working temperatures
- Low Thermal resistance
- Design can be adapted to many applications, dimensions and requests
Several technologies are available
- FSW (Friction Stir Welding) liquid Cold plates
- Vacuum brazed liquid cold plates (aluminum or stainless steel)
- Embedded tubes
- Copper brazed cold plates
- Drilled chanels
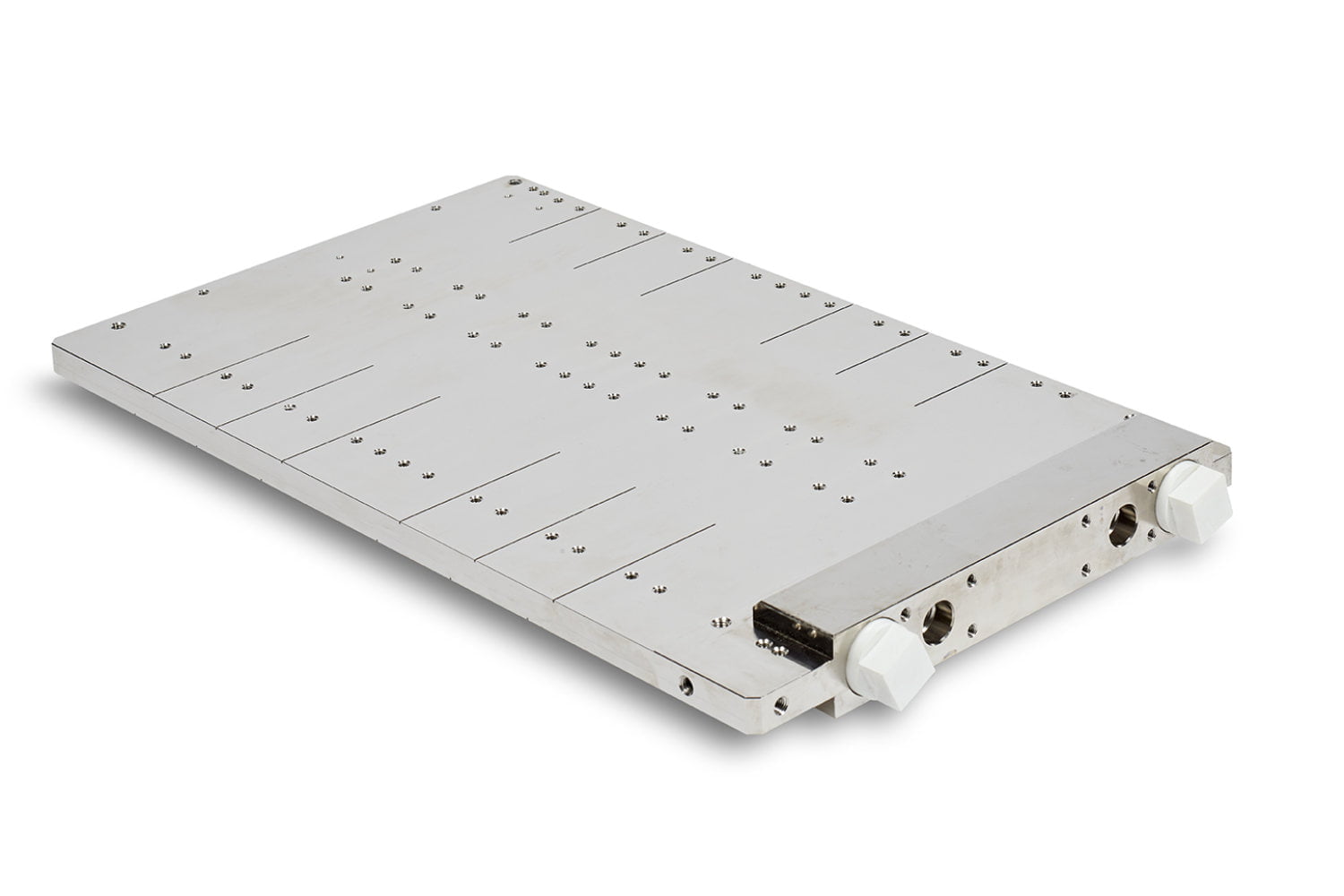
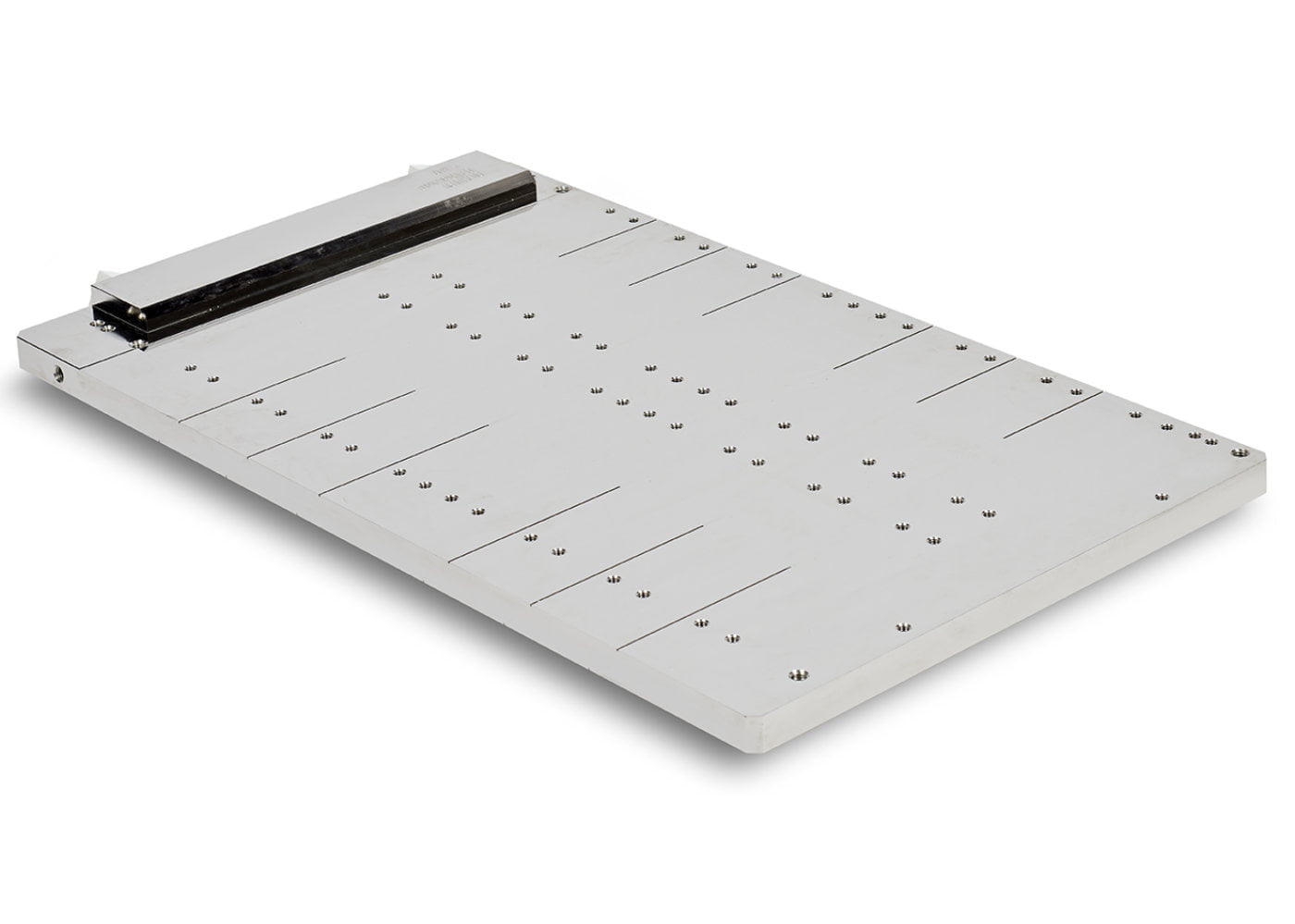
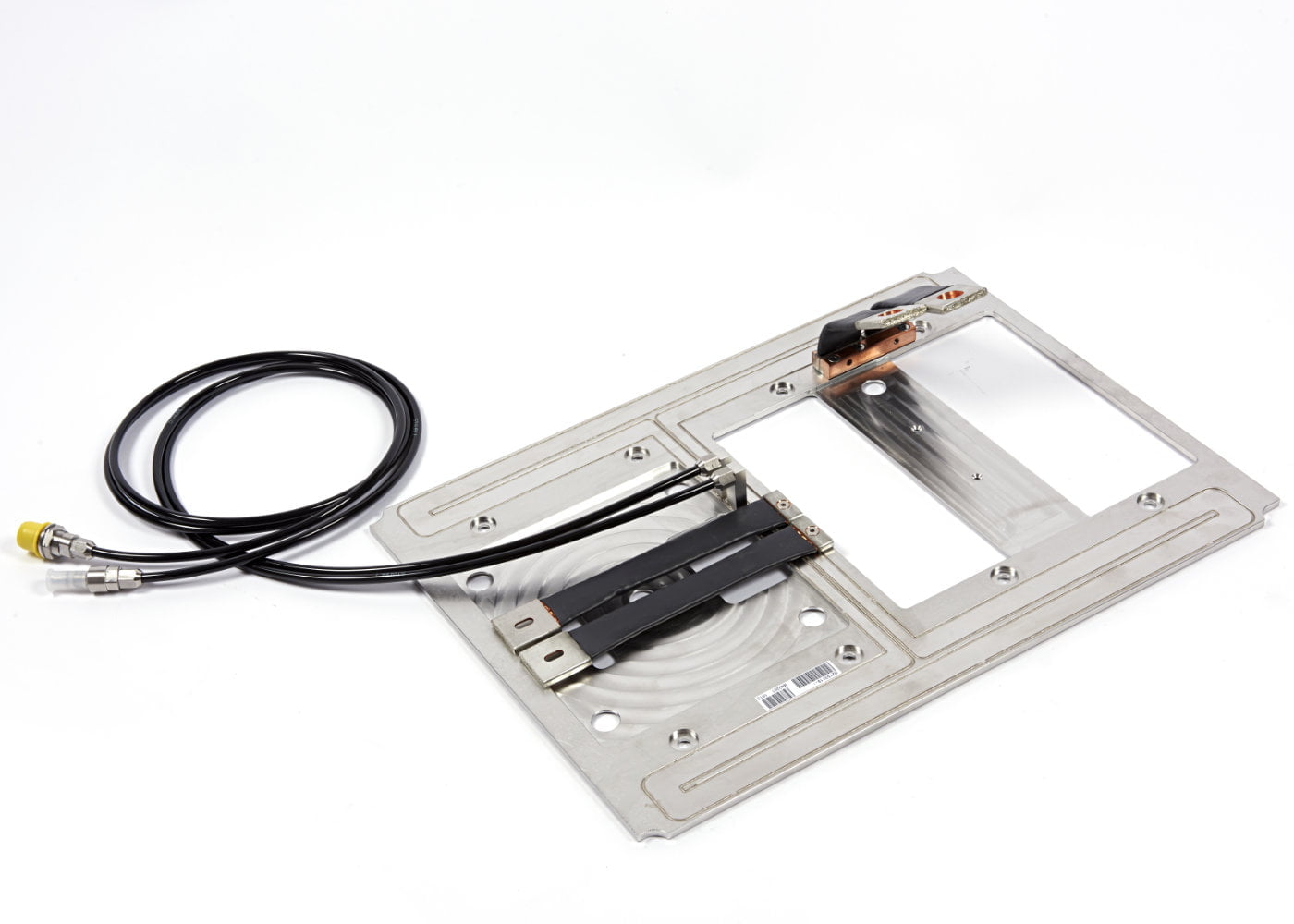
Vacuum brazed liquid cold plates
Aluminium brazing allows smart parts assemblies. This process is usually performed in controlled or under vacuum atmosphere. Brazed cold plates are very interesting for complex and efficient applications.
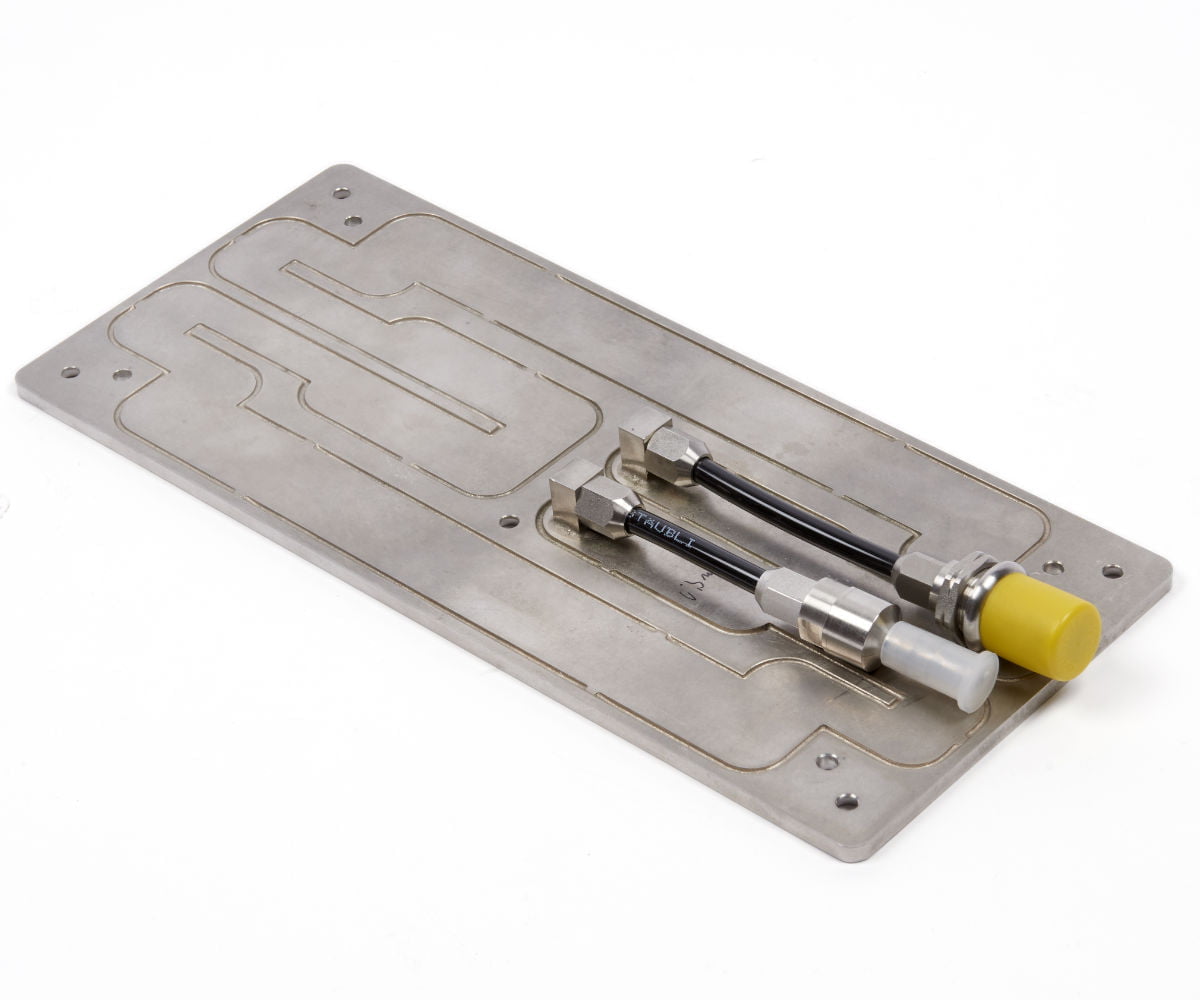
Fluid channels are milled on a base plate, according components map. Thermal features can be integrated under the components to increase the thermal efficiency and temperature homogeneity.
Cover is brazed on the milled face in order to close the cold plate.
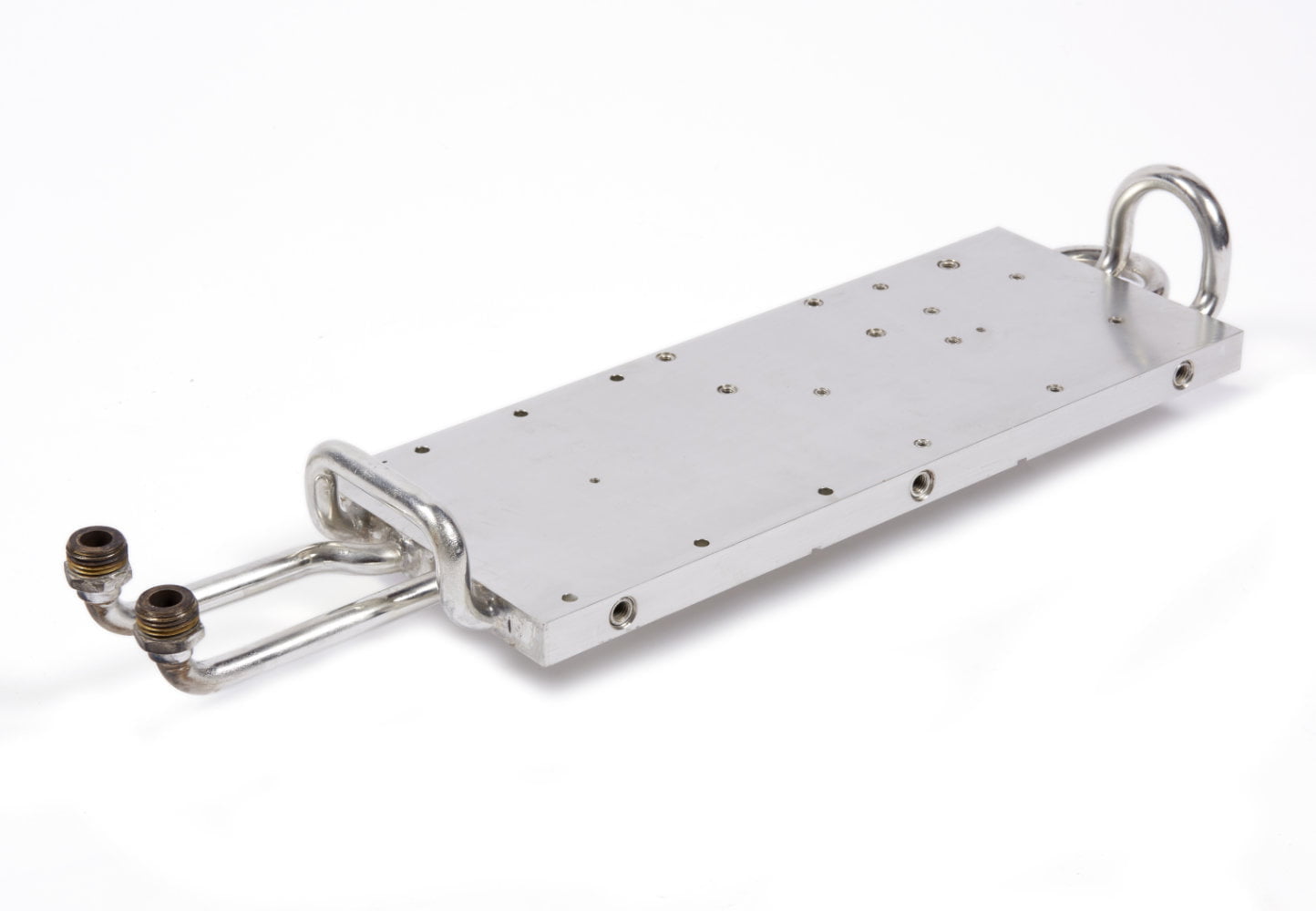
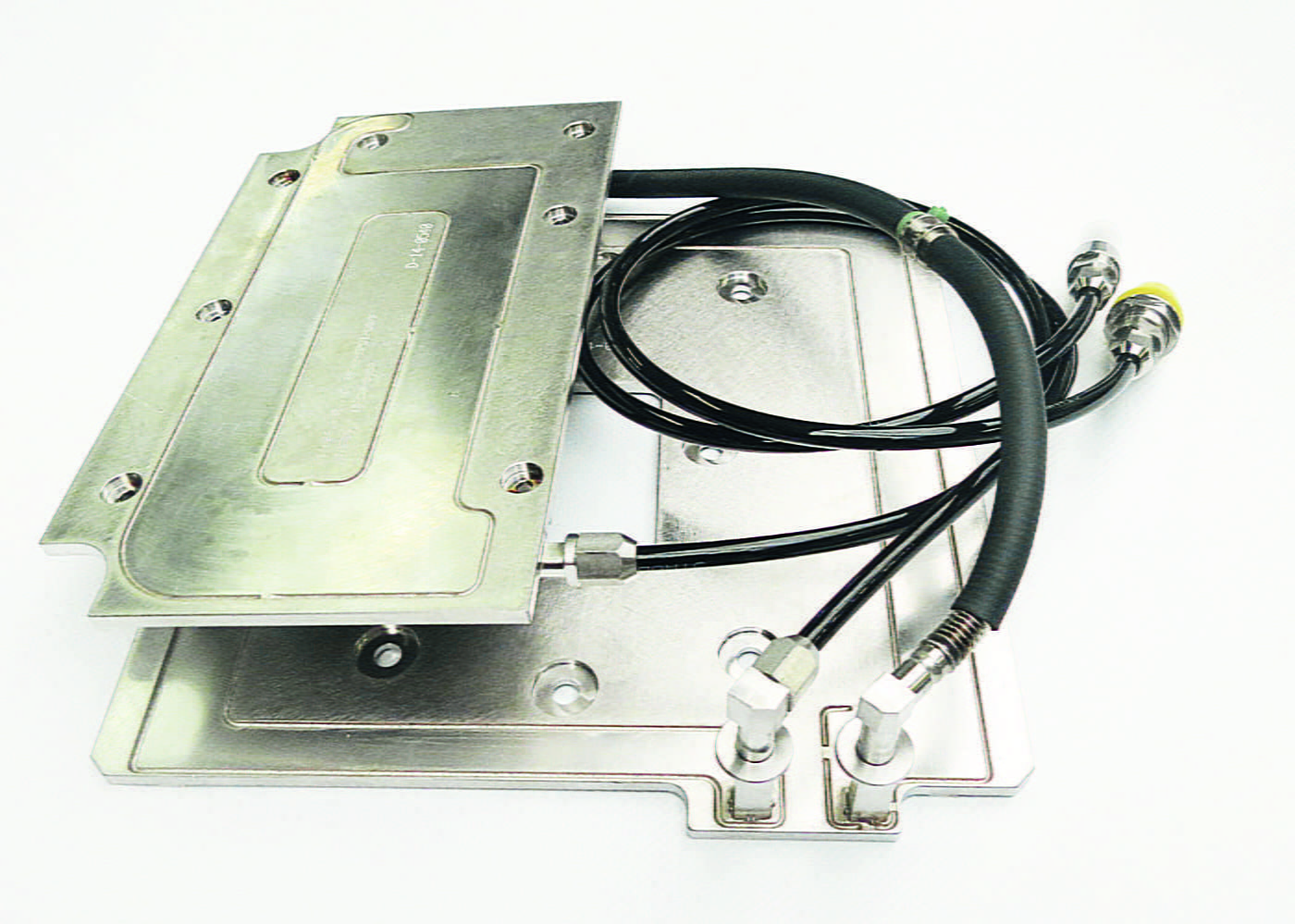
Cold plates with embedded tubes
Embeded cold plates are made by assembly of a bent tube and a base plate. The electronic components are set up on the base plate.
Tubes can be made of aluminium, copper or stainless steel and are usually assembled by pressing, brazing or additioning a thermal compound (thermal glue).